Sick right now? Flu is resurging to yet a higher peak this season.
While H5N1 bird flu ratchets up anxiety and egg prices, seasonal influenza viruses are rallying to a second high this winter, an uncommon course not seen in most years.
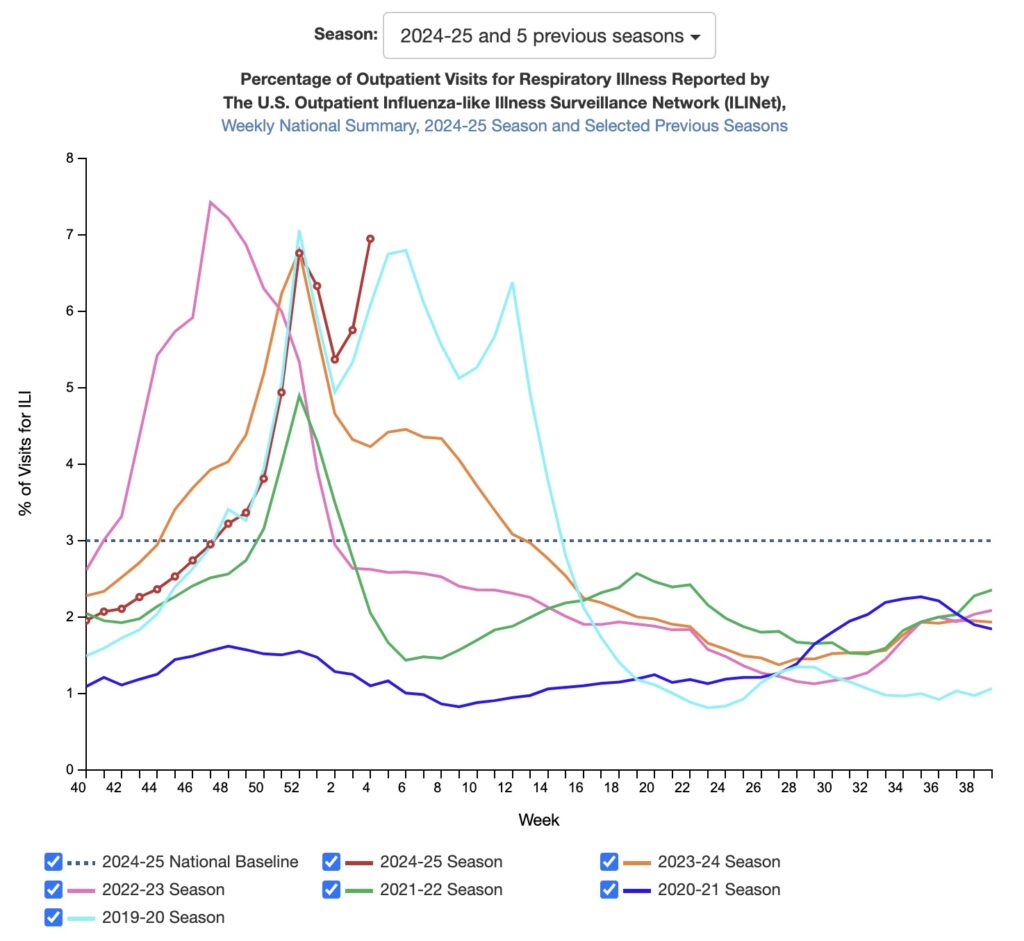
Flu cases had previously peaked this season at the very end of December. At week 52—ending on December 28—the percentage of outpatient visits related to influenza-like illnesses (ILI) hit about 6.76 percent, then ticked down the first week of 2025 (week 1). The percentage of ILI visits is the standard metric for tracking flu activity, which tends to peak at around 7 percent or lower in a given season. The 2009–2010 flu season—when the novel H1N1 (aka swine flu) emerged—stands out for hitting a decades' high of 7.7 very early in the season (week 42).
 Credit:
CDC
Credit:
CDC


© Getty | Christina House