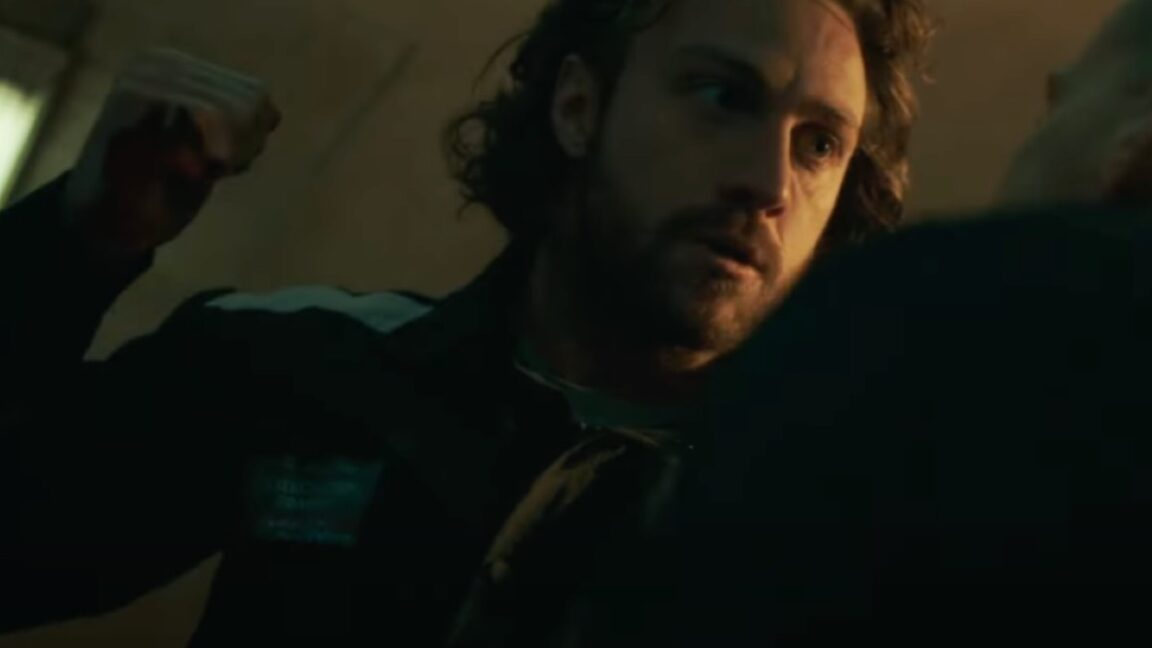
The physics of ugly Christmas sweaters
'Tis the season for many holiday traditions, including the Ugly Christmas Sweater—you know, those 1950s-style heavy knits featuring some kind of cartoonish seasonal decoration, like snowflakes, Santa Claus, or—in the case of Mark Darcy from Bridget Jones' Diary (2001)—Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer. "It’s obnoxious and tacky, but also fuzzy and kind of wholesome—the fashion equivalent of a Hallmark Christmas movie (with a healthy dose of tongue-in-cheek)," as CNN's Marianna Cerini recently observed.
Fashion (or lack thereof) aside, sweaters and other knitted fabric are also fascinating to physicists and mathematicians. Case in point: a recent paper published in the journal Physical Review Letters examining the complex mechanics behind the many resting shapes a good Jersey knit can form while at rest.
Knitted fabrics are part of a class of intertwined materials—which also includes birds' nests, surgical knots, knotted shoelaces, and even the degradation of paper fibers in ancient manuscripts. Knitted fabrics are technically a type of metamaterial: an engineered material that gets its properties not from the base materials but from their designed structures. The elasticity (aka, stretchiness) of knitted fabrics is an emergent property: the whole is more than the sum of its parts. How those components (strands of yarn) are arranged at an intermediate scale (the structure) determines the macro scale properties of the resulting fabric.
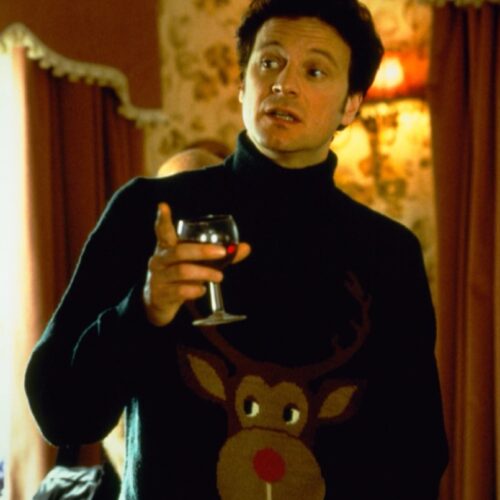
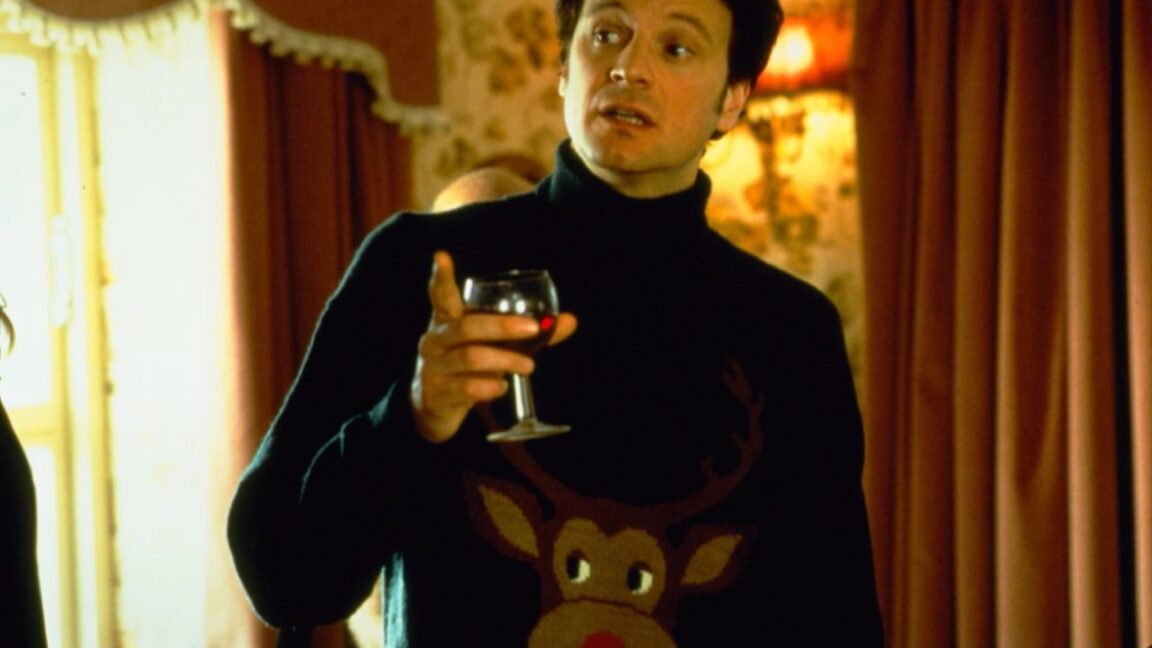


© Miramax Films