The New Doctor Who Trailer Introduces His Latest Partner in Time
Doctor Who returns with new episodes and his fresh new companion Belinda Chandra beginning April 12.

The World Health Organization has begun cost-cutting measures in preparation for a US withdrawal next year, according to reporting by Reuters.
On his first day in office, President Trump signed an executive order to withdraw the US from the United Nation's health agency. The country was a founding member of the WHO in 1948 and has since been a key member of the organization, which has 193 other member states. The executive order cited Trump's long-standing complaints about the agency's handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, dues payments, and alleged protection of China as the reasons for the withdrawal.
In a statement on Tuesday, the WHO said it "regrets" the announcement and hopes the US will reconsider.


© Getty | FABRICE COFFRINI
On his first day in office, President Trump issued an executive order to withdraw the US from the World Health Organization, a process that requires a one-year notice period as set out in a 1948 Joint Resolution of Congress.
Trump initially tried to extract the US from the United Nations health agency in July 2020, but the process did not come to completion before he was voted out of office.
At the time, Trump criticized the agency's handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, claimed it was protecting China, and asserted that it was overcharging the US in dues. "China has total control over the World Health Organization despite only paying $40 million per year, compared to what the United States has been paying, which is approximately $450 million a year," Trump said in 2020 prior to issuing the first notice of withdrawal.


© Getty | Fabrice Cof

There's a good chance you've seen headlines about HMPV recently, with some touting "what you need to know" about the virus, aka human metapneumovirus. The answer is: not much.
It's a common, usually mild respiratory virus that circulates every year, blending into the throng of other seasonal respiratory illnesses that are often indistinguishable from one another. (The pack includes influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus, parainfluenza virus, common human coronaviruses, bocavirus, rhinovirus, enteroviruses, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae, among others.) HMPV is in the same family of viruses as RSV.
As one viral disease epidemiologist at the US Centers for Disease Control summarized in 2016, it's usually "clinically indistinguishable" from other bog-standard respiratory illnesses, like seasonal flu, that cause cough, fever, and nasal congestion. For most, the infection is crummy but not worth a visit to a doctor. As such, testing for it is limited. But, like other common respiratory infections, it can be dangerous for children under age 5, older adults, and those with compromised immune systems. It was first identified in 2001, but it has likely been circulating since at least 1958.


© Getty | Li Hongbo
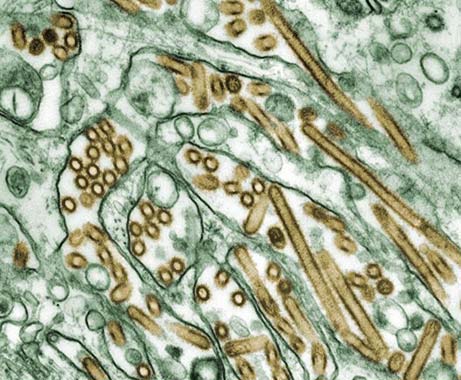
The H5N1 bird flu situation in the US seems more fraught than ever this week as the virus continues to spread swiftly in dairy cattle and birds while sporadically jumping to humans.
On Monday, officials in Louisiana announced that the person who had developed the country's first severe H5N1 infection had died of the infection, marking the country's first H5N1 death. Meanwhile, with no signs of H5N1 slowing, seasonal flu is skyrocketing, raising anxiety that the different flu viruses could mingle, swap genetic elements, and generate a yet more dangerous virus strain.
But, despite the seemingly fever-pitch of viral activity and fears, a representative for the World Health Organization today noted that risk to the general population remains low—as long as one critical factor remains absent: person-to-person spread.


© uafcde
