China is having standard flu season despite widespread HMPV fears
There's a good chance you've seen headlines about HMPV recently, with some touting "what you need to know" about the virus, aka human metapneumovirus. The answer is: not much.
It's a common, usually mild respiratory virus that circulates every year, blending into the throng of other seasonal respiratory illnesses that are often indistinguishable from one another. (The pack includes influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), adenovirus, parainfluenza virus, common human coronaviruses, bocavirus, rhinovirus, enteroviruses, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae, among others.) HMPV is in the same family of viruses as RSV.
As one viral disease epidemiologist at the US Centers for Disease Control summarized in 2016, it's usually "clinically indistinguishable" from other bog-standard respiratory illnesses, like seasonal flu, that cause cough, fever, and nasal congestion. For most, the infection is crummy but not worth a visit to a doctor. As such, testing for it is limited. But, like other common respiratory infections, it can be dangerous for children under age 5, older adults, and those with compromised immune systems. It was first identified in 2001, but it has likely been circulating since at least 1958.
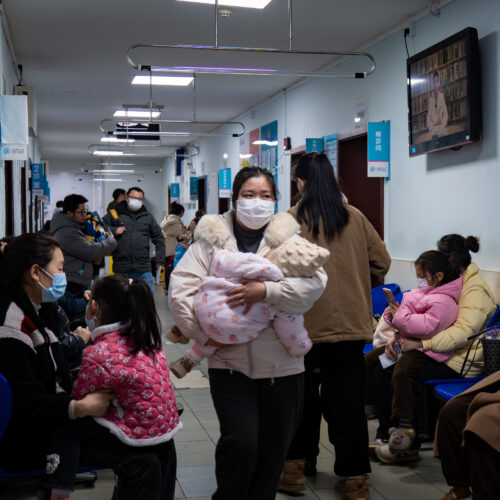
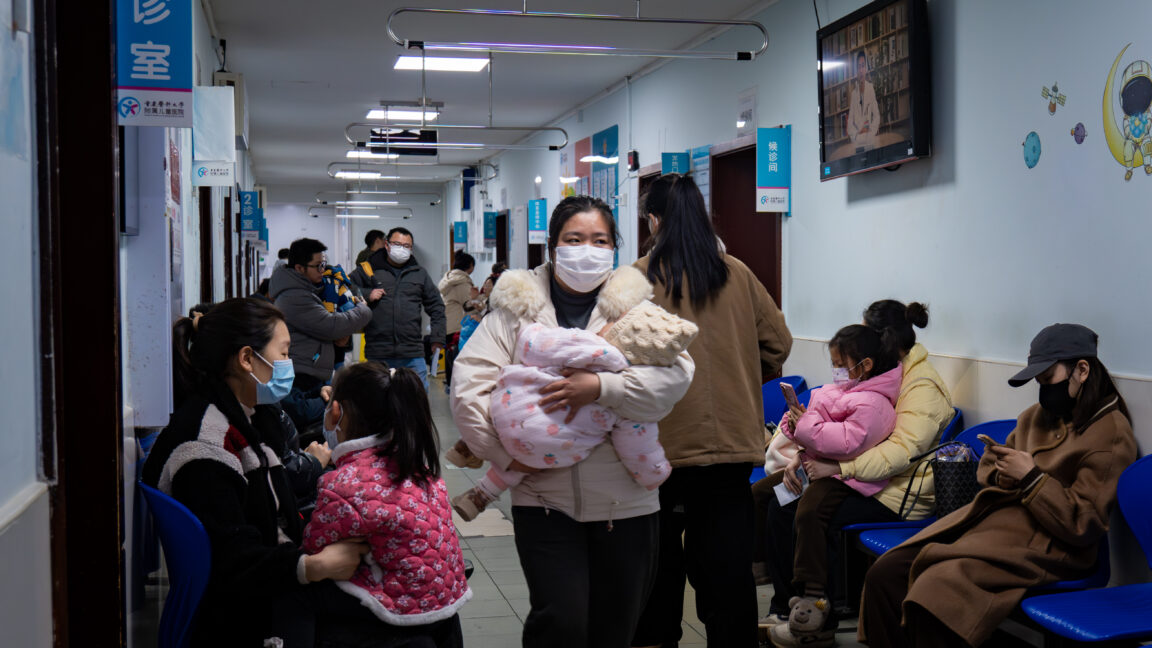


© Getty | Li Hongbo