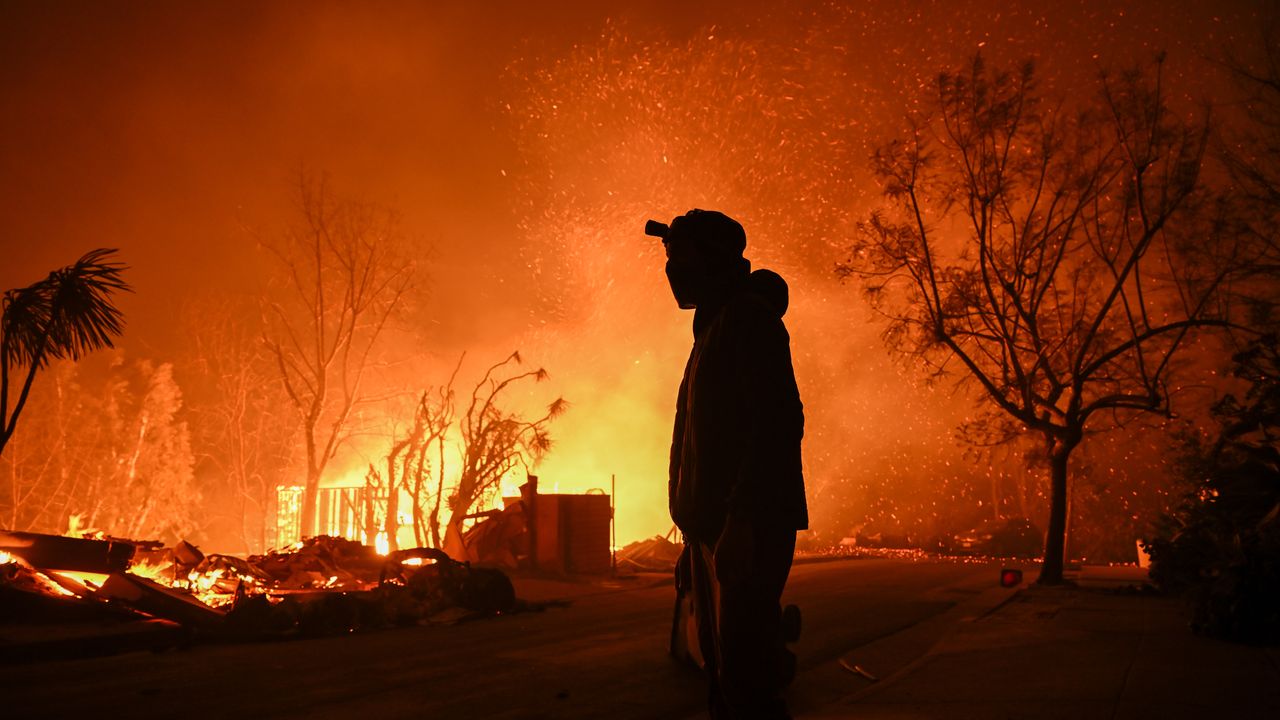
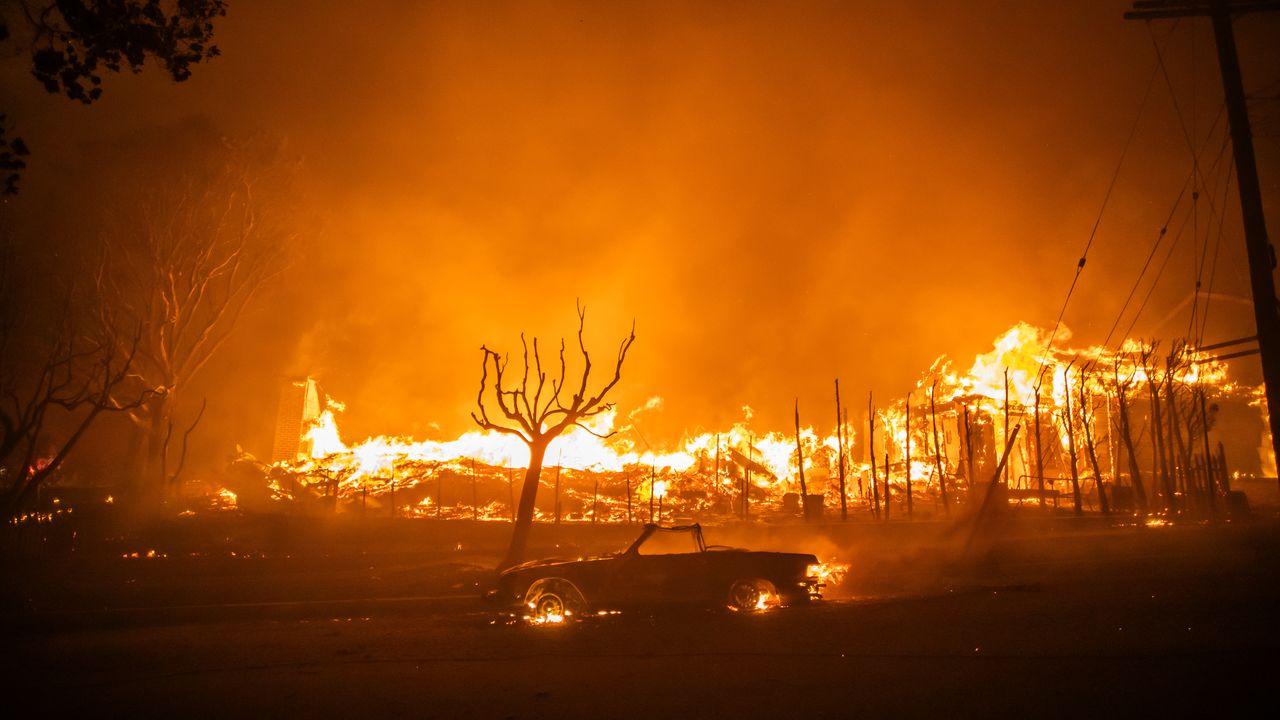
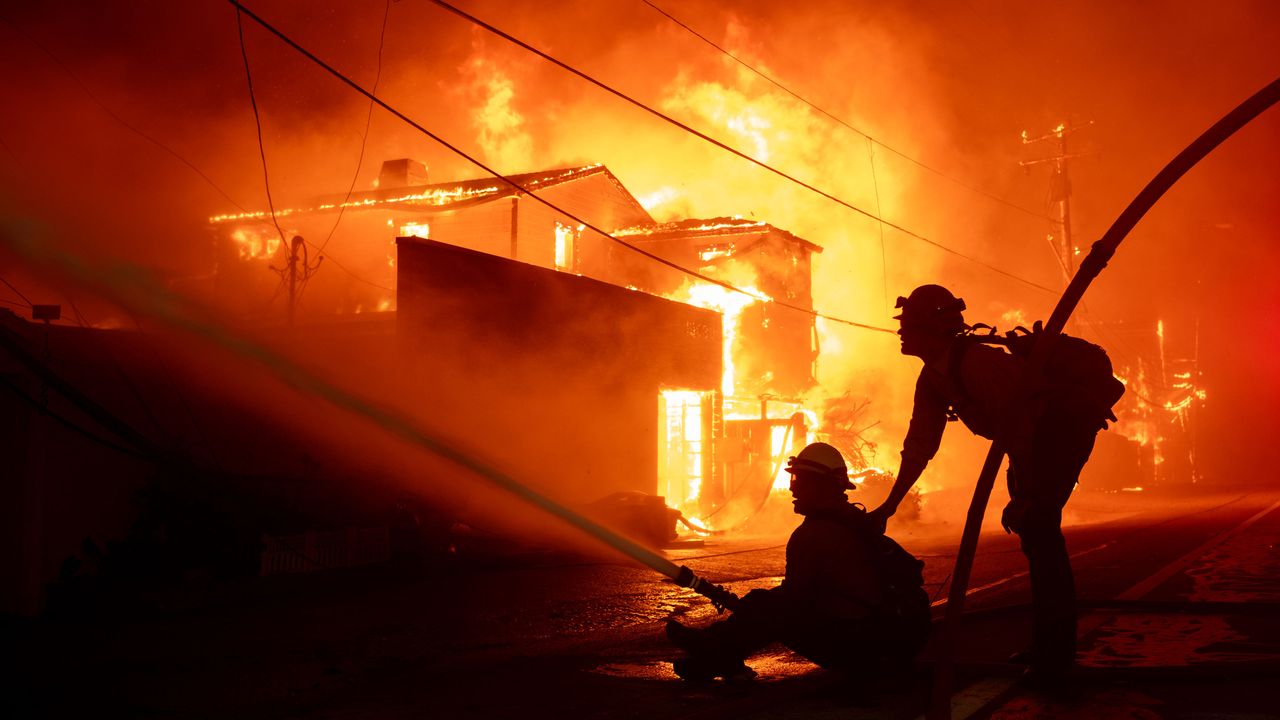
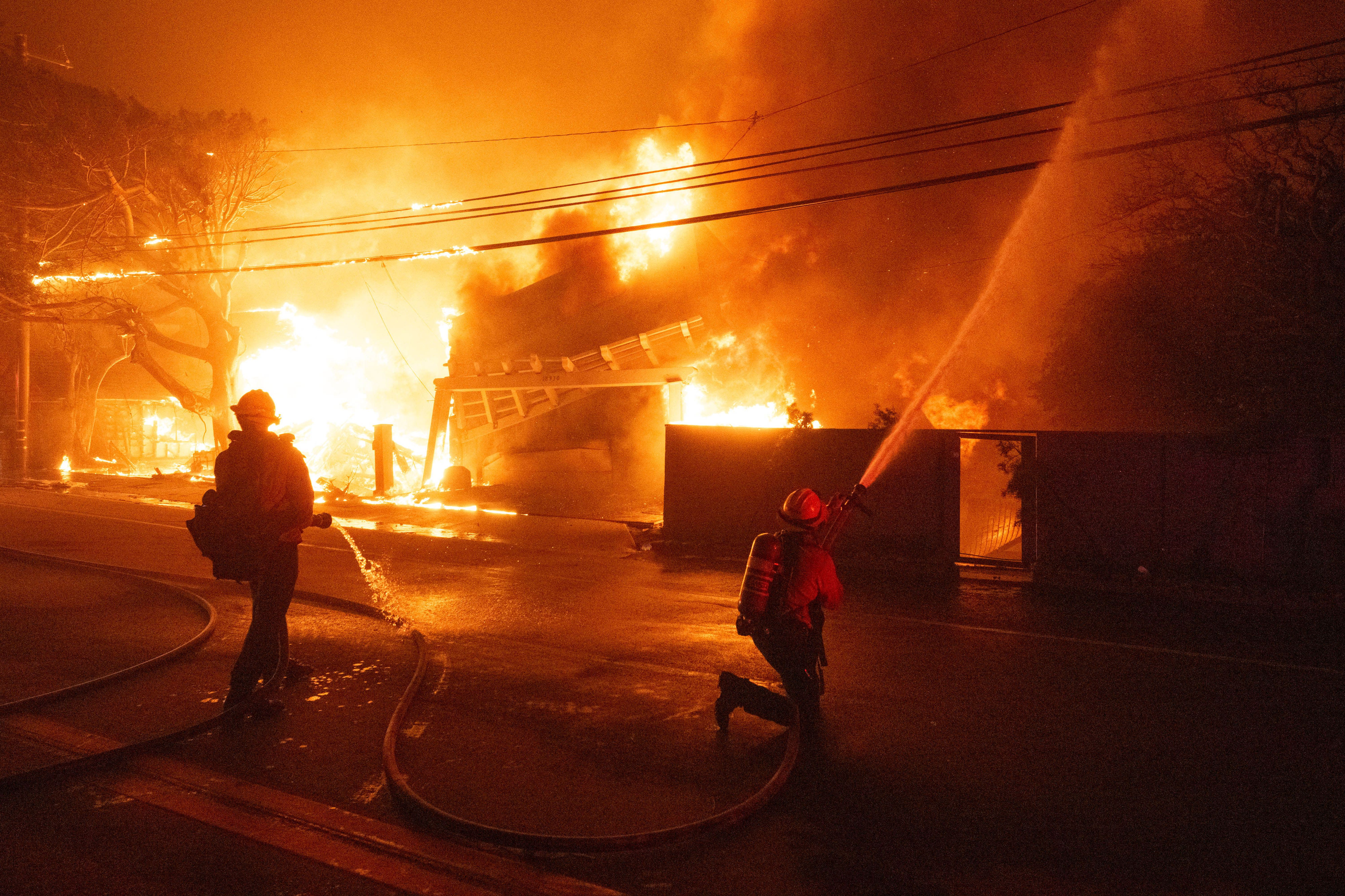
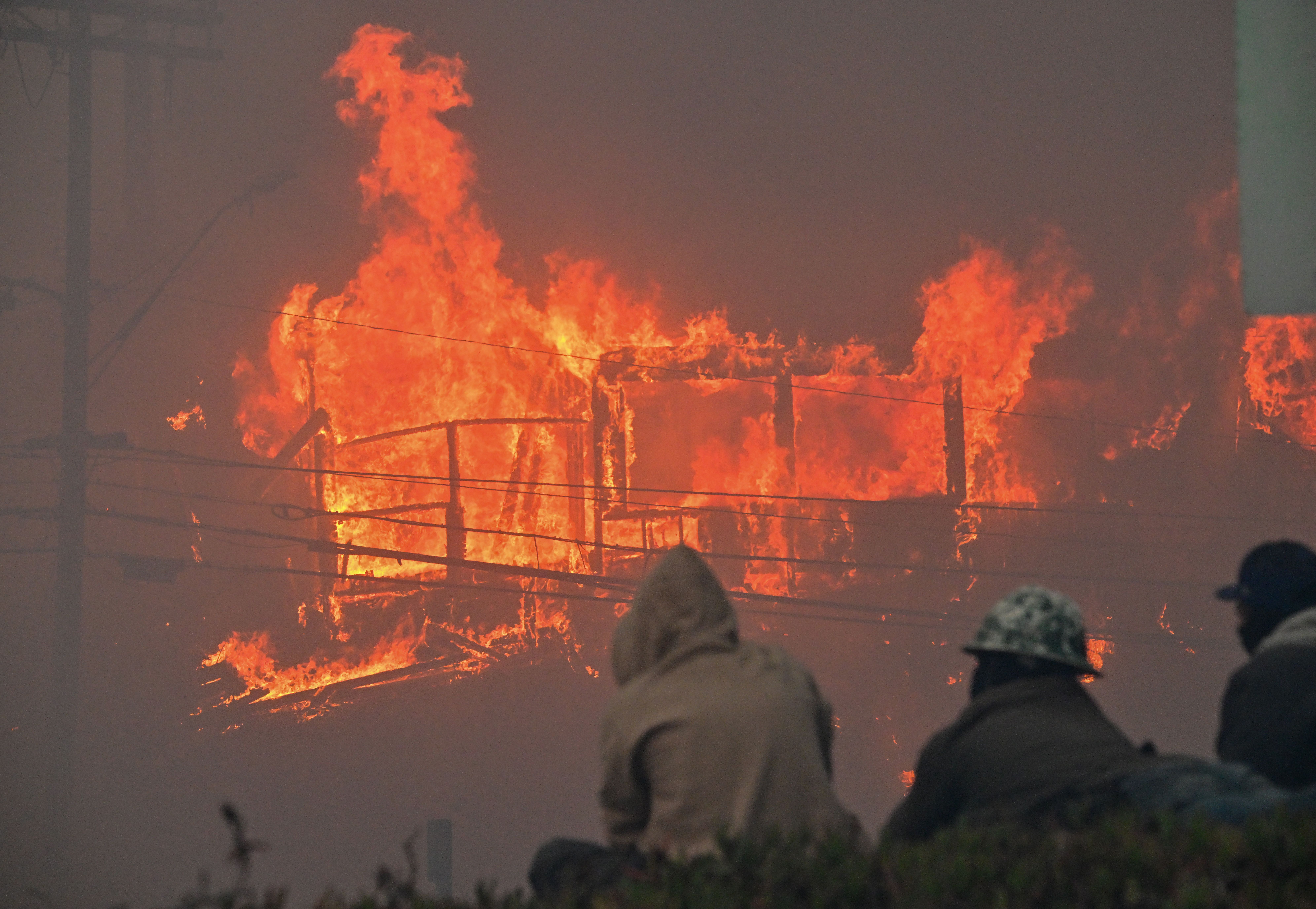
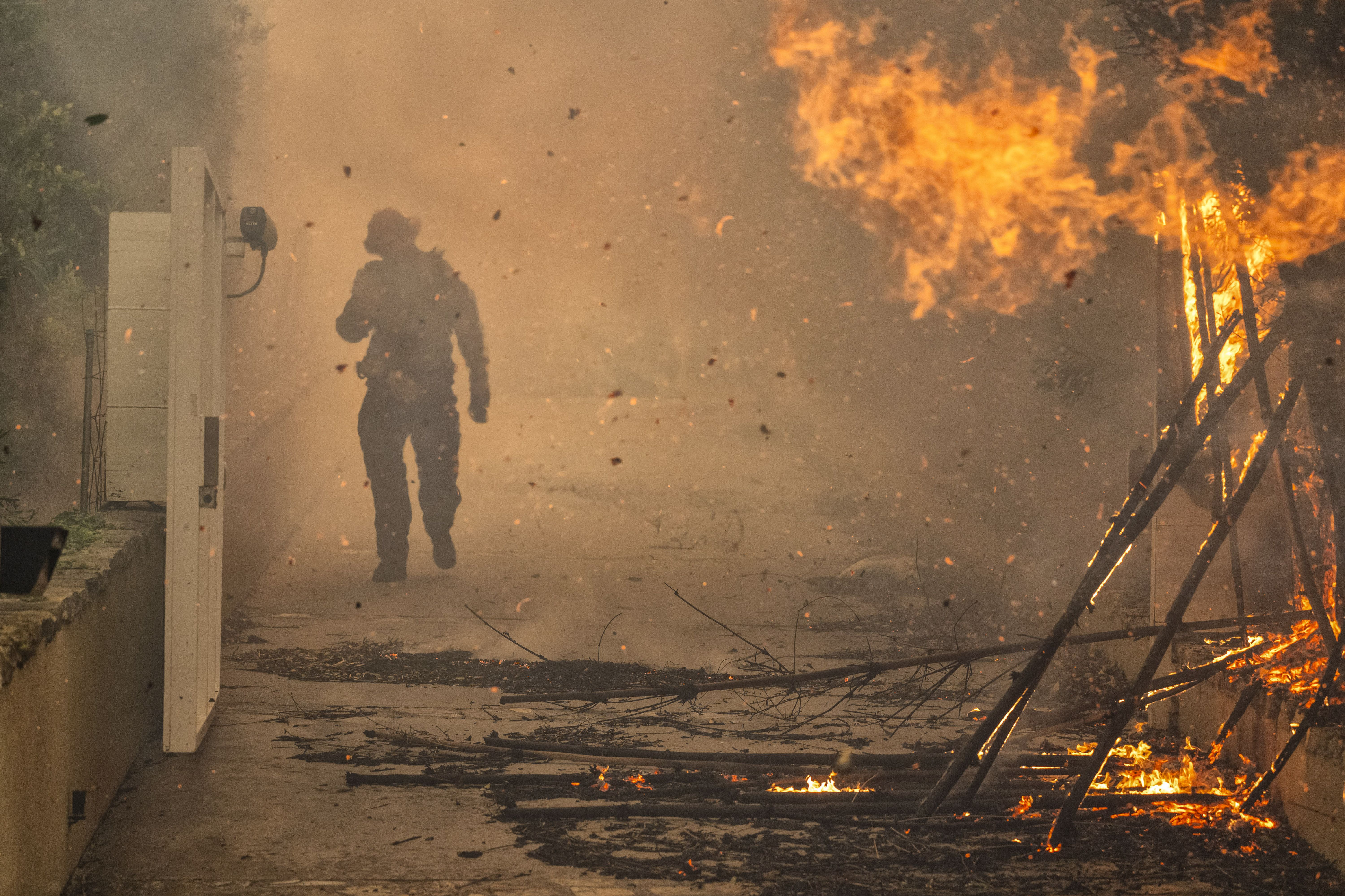
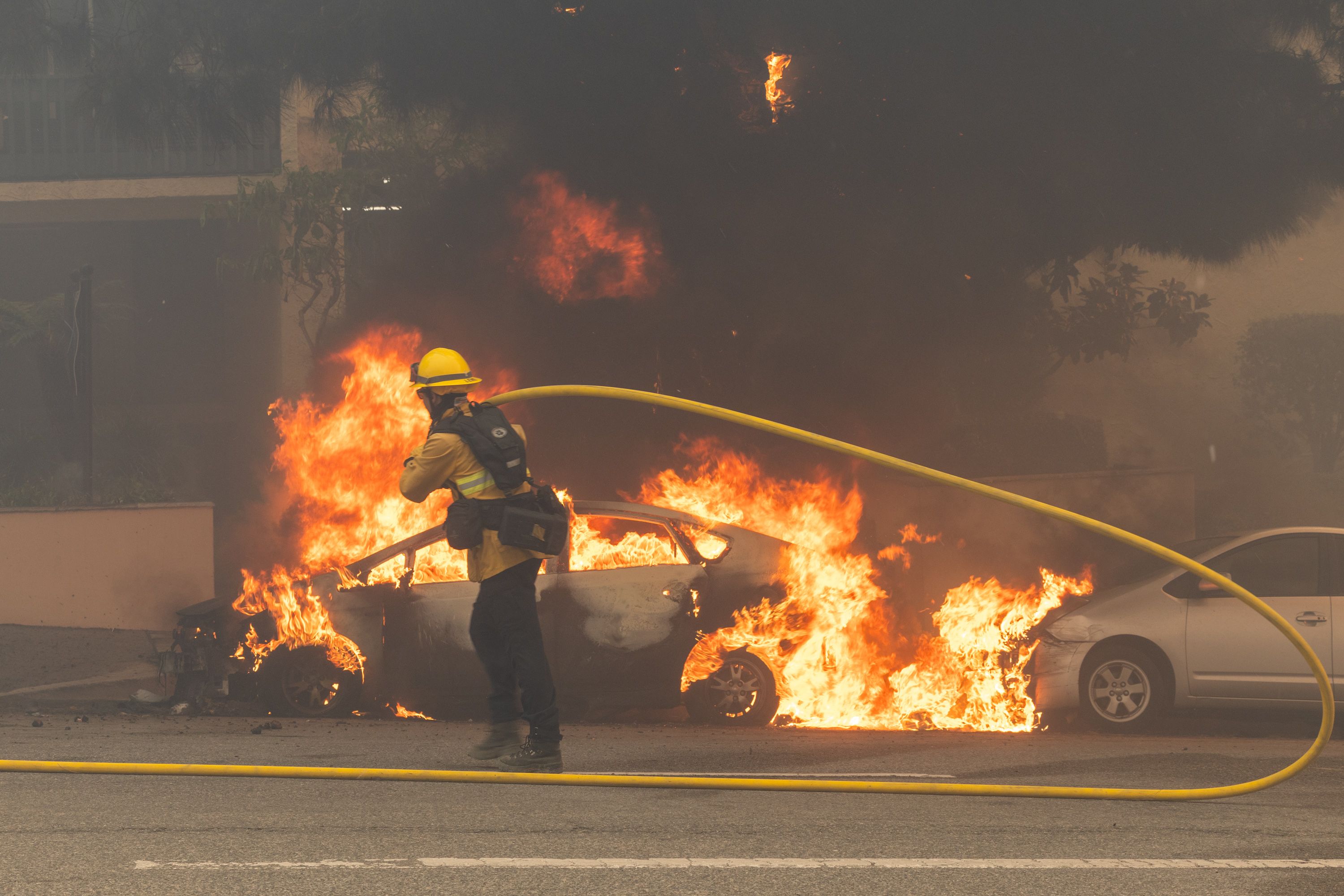
Why LA wildfires forecasts alone couldn't stop the death toll
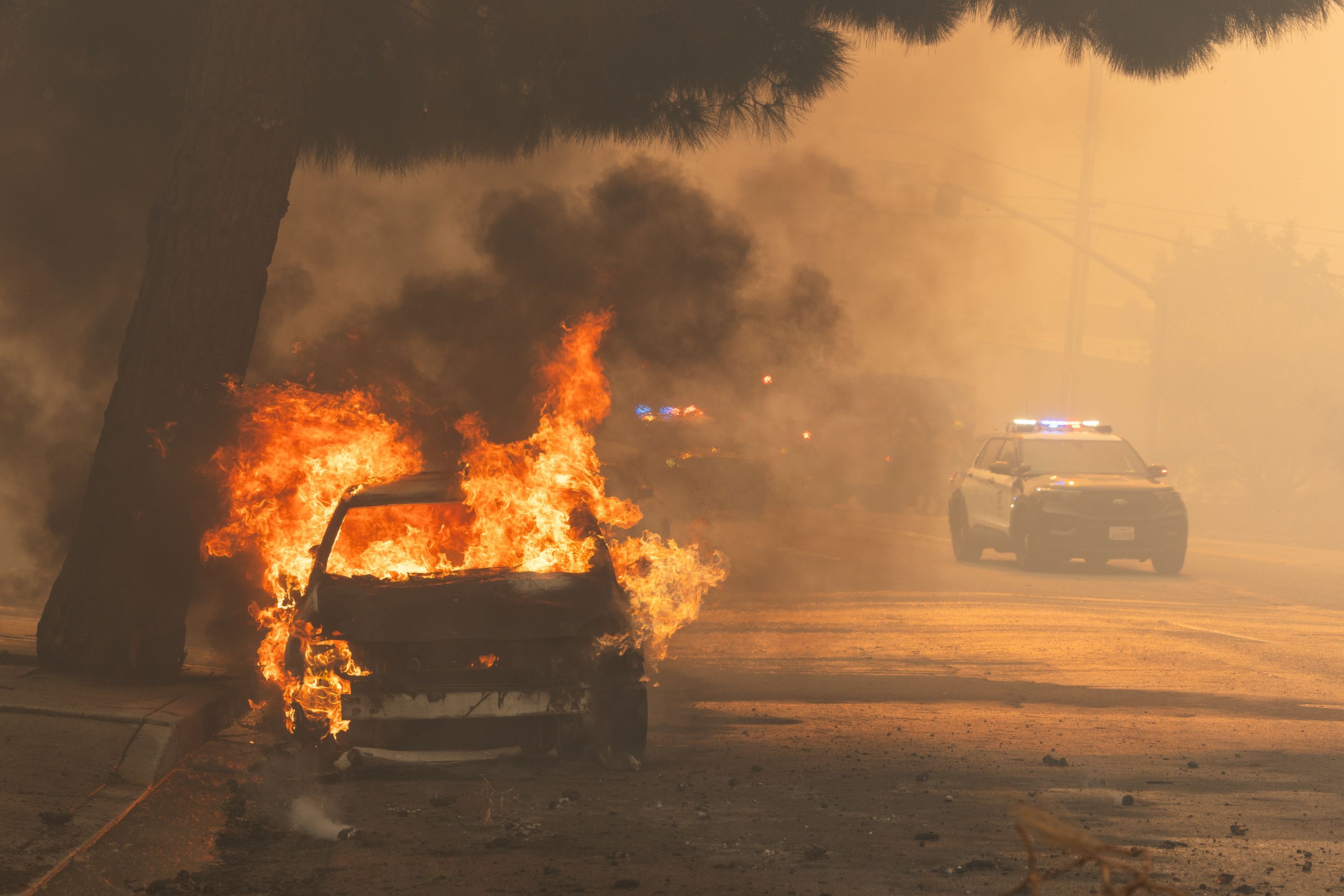
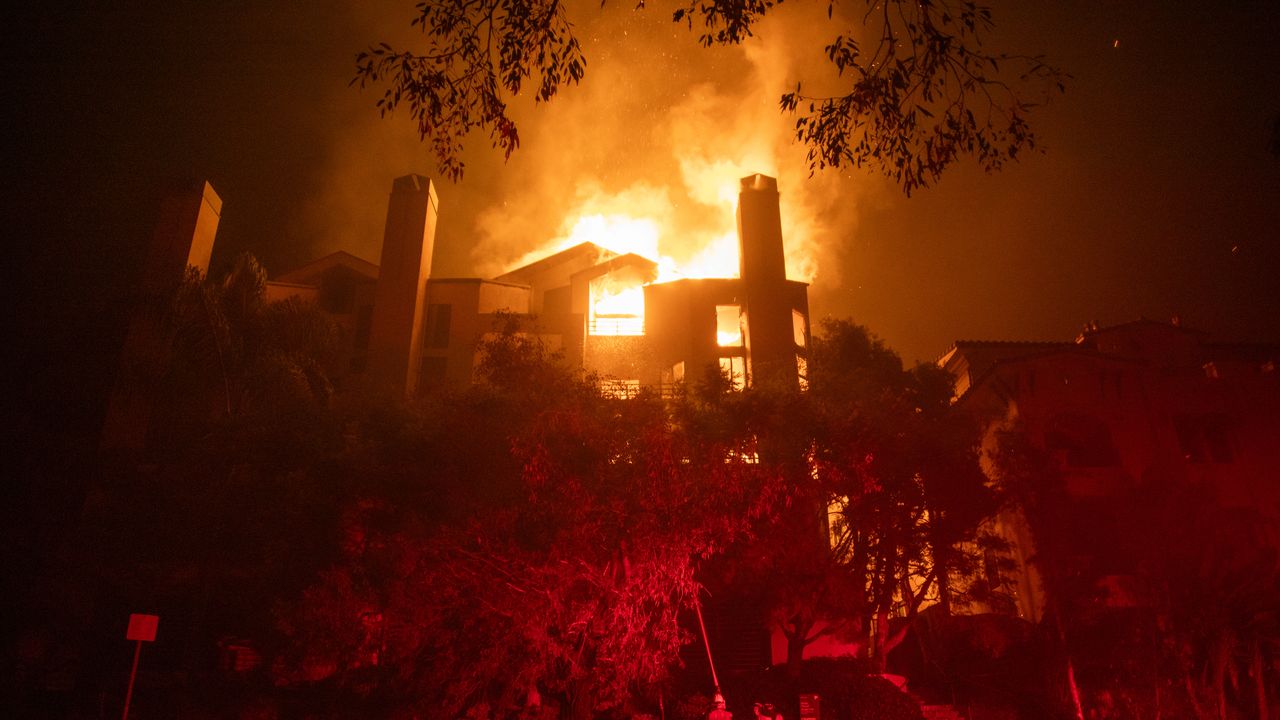
The deadly Los Angeles area fires show what can go horribly wrong even when weather forecasts and warnings prove eerily prescient.
Why it matters: Weather forecasters are struggling with how to communicate the dangers of extreme weather events as those events increase in frequency and ferocity with human-caused climate change.
- This involves a mix of meteorology and climate science, along with social science research into how people respond to warning language and official advice.
The big picture: It's unclear if the public fully grasps the meaning of the National Weather Service's fire weather warnings or the criteria behind its terms, Stephen Bieda, chief of the service's Severe, Fire, Public and Winter Weather Services Branch, told Axios.
- "There is a larger-scale conversation going on" about better aligning NWS' products with input from communications and social science professionals, he said.
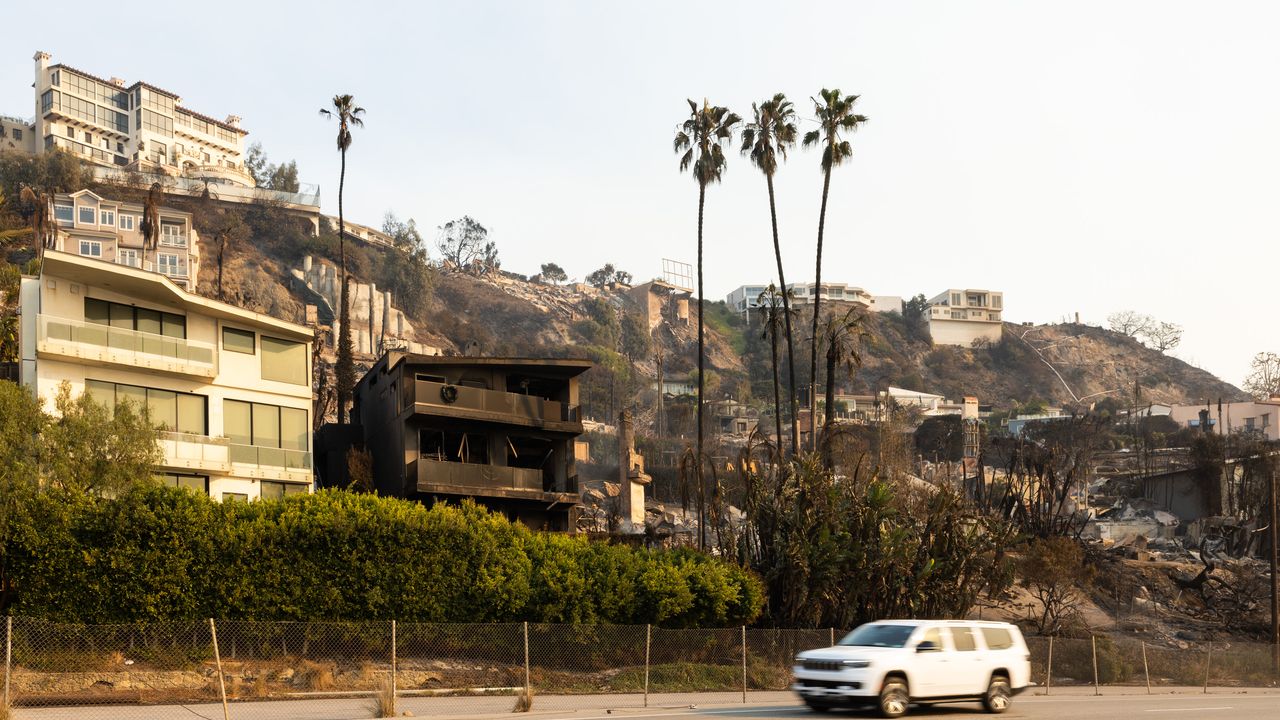
Zoom in: There are some eerie similarities between the firestorm that began to engulf portions of LA County on Jan. 7 and recent hurricanes — such as Ian and Helene — that were accurately forecast but still led to a large loss of life.
- In the case of Ian, some late shifts in the storm's path occurred, but it remained within the so-called "cone of uncertainty." Yet many were caught off guard when a storm surge roared across Sanibel Island and into Fort Myers Beach, killing dozens.
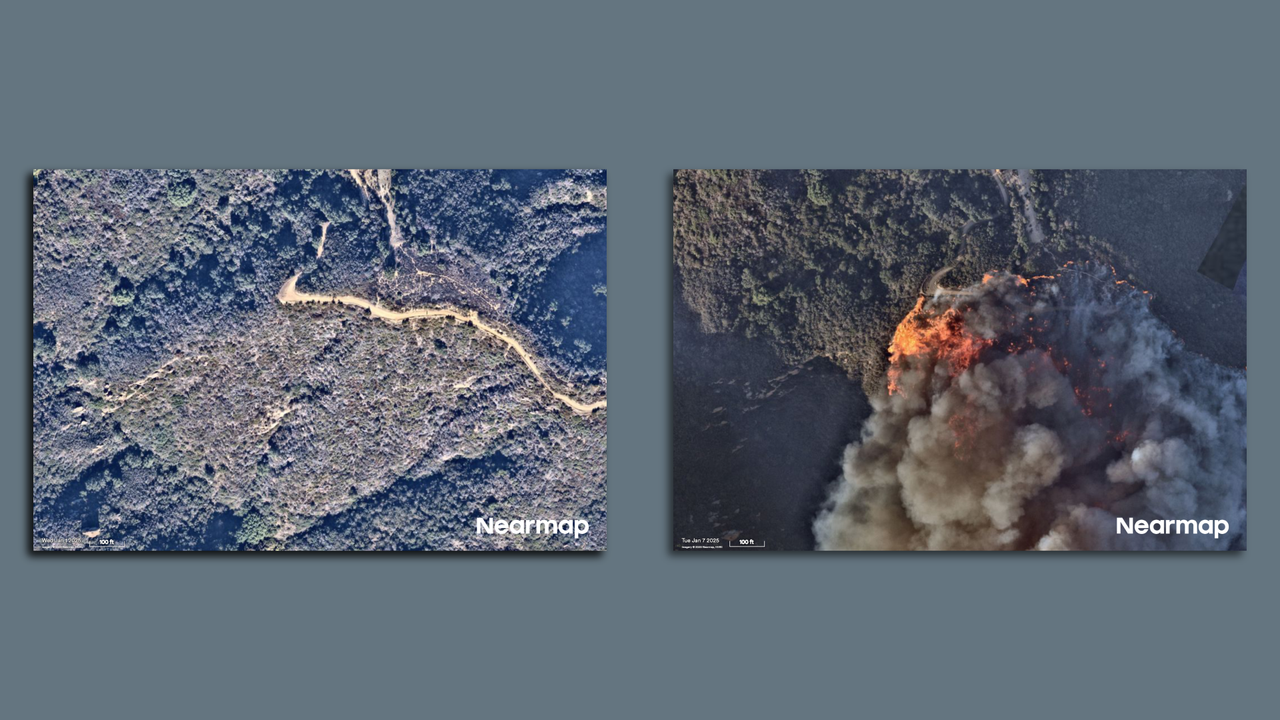
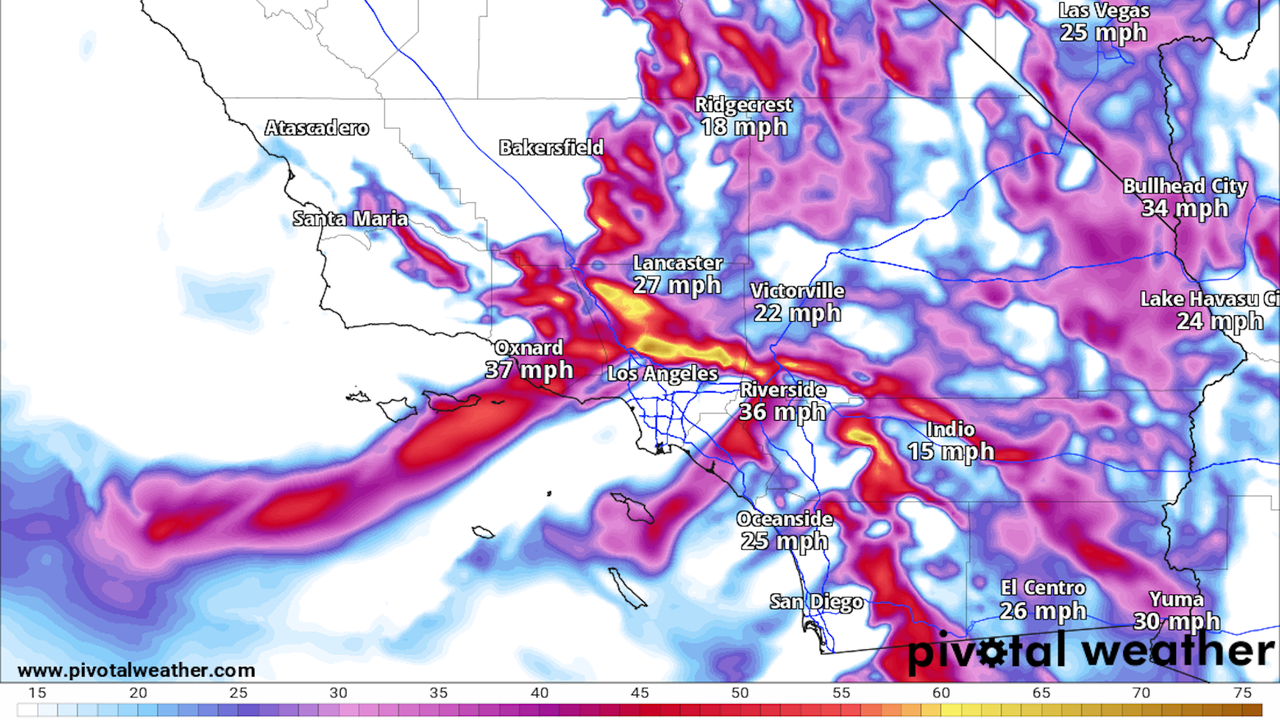
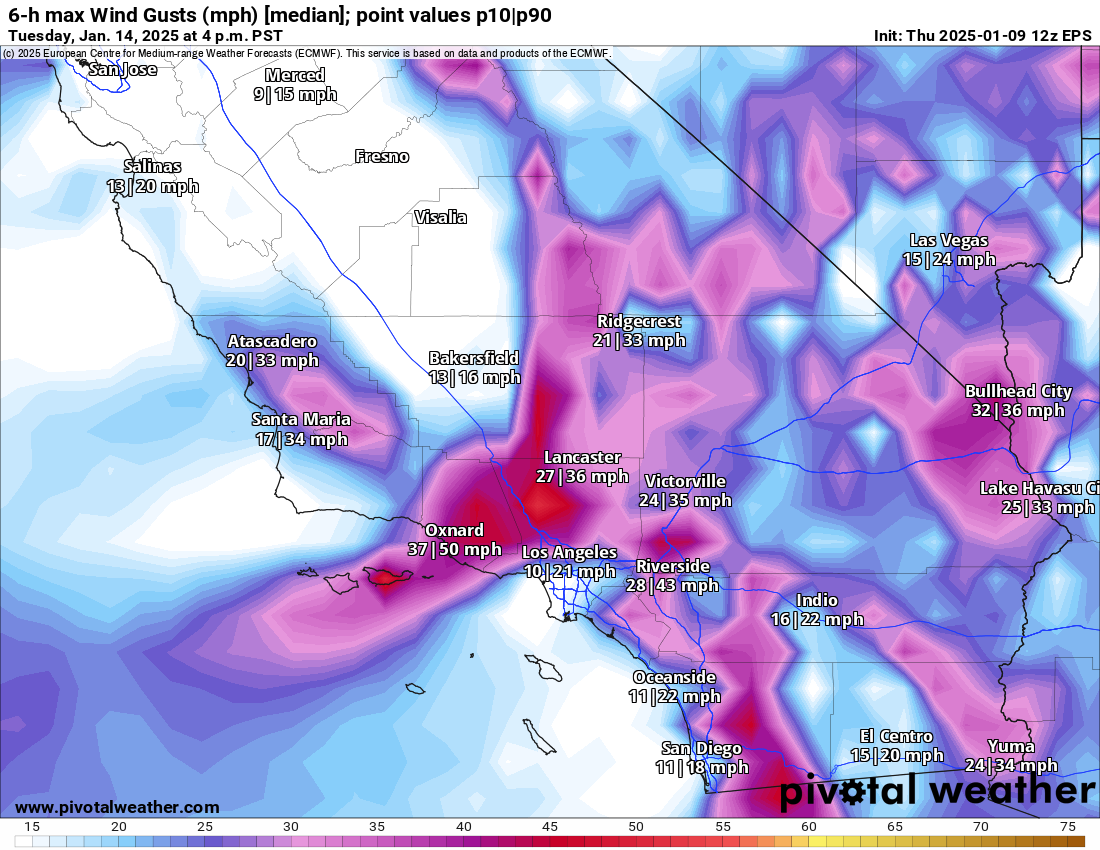
- The fires began during a period when the National Weather Service was practically screaming about the fire threat from a rare high wind event in ALL CAPS text.
The consensus was that any fire start could grow "explosively" and be nearly impossible to contain even with the pre-staging of fire crews.
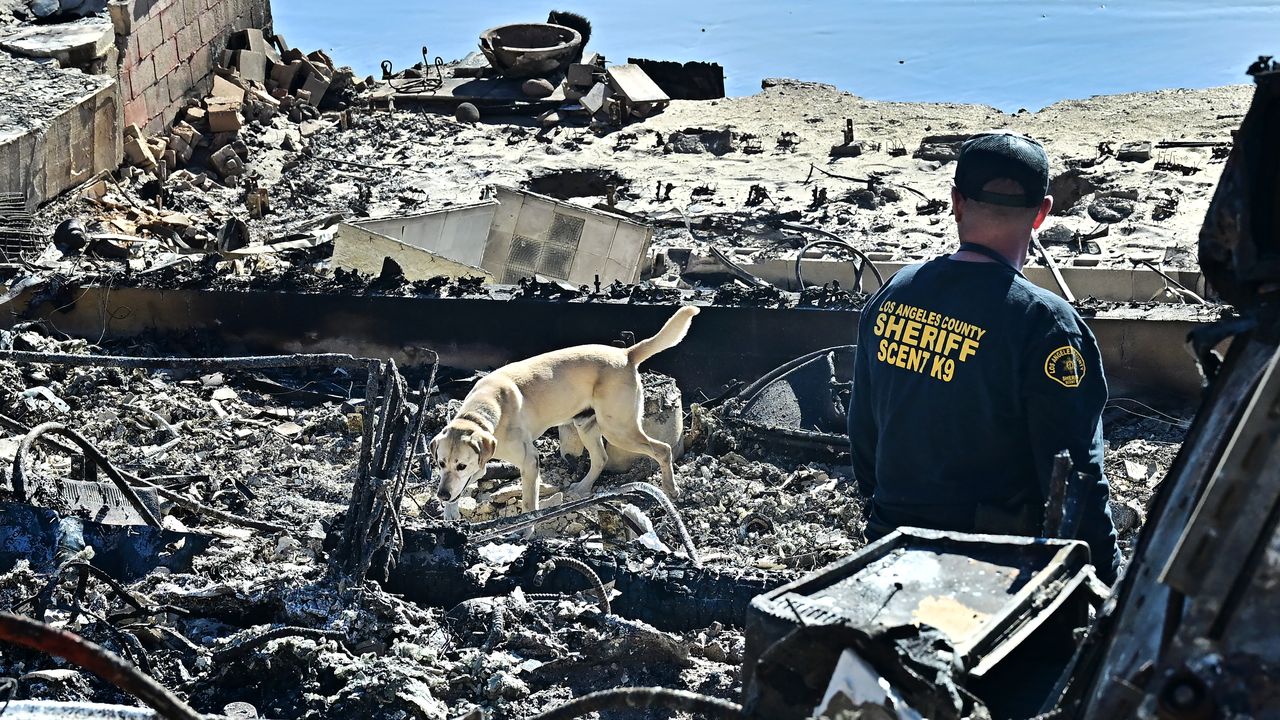
- Sadly, four such fires occurred around the same time, overwhelming responders, many of whom had been prepositioned to act quickly.
Context: Red flag warnings were initially created for emergency managers and land management agencies in the 1990s, Bieda said.
- Similarly, "Particularly Dangerous Situation" Red Flag warnings were implemented about five years ago — again primarily for the emergency management community to increase readiness rather than the public.
- But, given the accessibility of information, those warnings are widely consumed, Bieda said.
- He said their basic message is that forecasters have the highest-possible confidence that a worst-case combination of dry vegetation, or fuels, and strong winds will occur to produce a potentially devastating event.
Friction point: According to Amanda Stasiewicz, a researcher at the University of Oregon, and Stephanie Hoekstra, a wildfire social scientist at CIRA and NOAA, it's one thing to tell people to be prepared for potentially dire fire weather conditions.
- But pinpointing fire ignitions ahead of time isn't currently possible — and they said that may limit forecasts' utility.
- "You never know where the next fire is going to break out," Hoekstra told Axios. "Something that makes fires unique is that anywhere can be ground zero."
Both Stasiewicz and Hoekstra told Axios that so-called PDS Red Flag warnings are currently only used by some NWS forecast offices, including the LA office.
- They're geared mainly to partners of the NWS such as emergency management agencies and elected officials at the state, regional and local levels.
- Little research has been done on how they affect public preparation and response.
Between the lines: Social scientists who study responses to extreme weather watches and warnings — as well as evacuation orders — are limited by a lack of studies on wildfires, said Julie Demuth, who studies weather risks and decisions at the National Center for Atmospheric Research.
- "A major challenge we have with answering these questions is that we often don't have the social science 'observations' we need to answer these event-specific questions," she told Axios via email.
- Even evidence gleaned from other fire-prone areas is relatively sparse, Demuth and other experts told Axios.
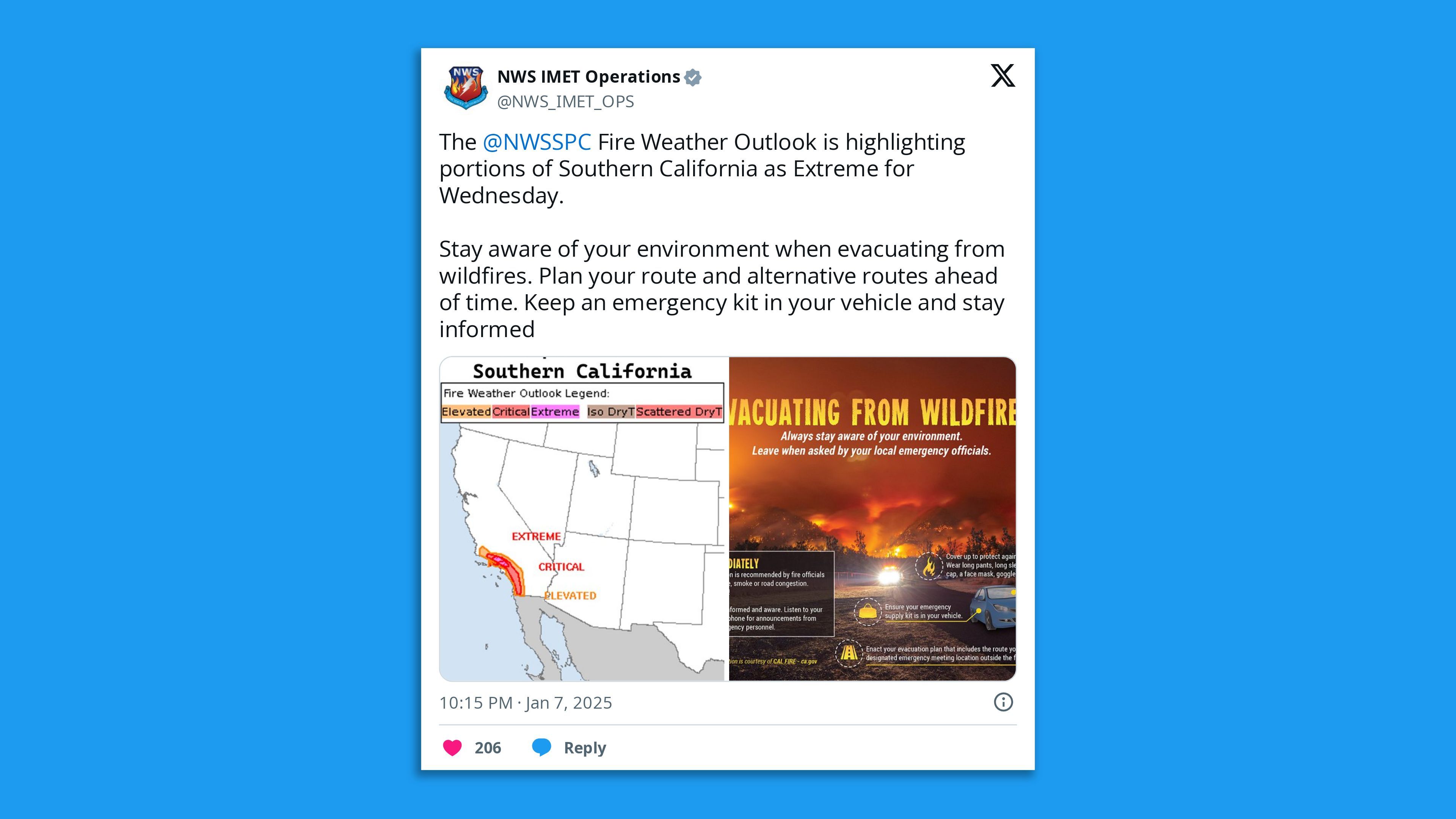
The intrigue: The NWS proactively anticipated the fire weather threat on Jan. 7, as well as the ongoing threat Tuesday through Wednesday.
- The first briefing for emergency managers on the Jan. 7 fire danger took place on New Year's Day, a Weather Service spokesperson said.
- The service's LA office began briefings the next day but had first mentioned the threat in its forecast products as early as Dec. 30.
- Watches and warnings were hoisted beginning four days in advance of the event, NOAA's timeline states.
What's next: Its potential shortcomings aside, the Weather Service's most dire fire weather warning, the PDS Red Flag Warning, is in effect for parts of LA and Ventura Counties through Wednesday at noon.
Go deeper:
Climate change plays key contributing role in LA fires
New, rare fire warning issued in Southern California
The psychological toll of California's catastrophic fires