New York Man Digs Up Mastodon Fossil in His Backyard

The proboscidean's jaw was found about 70 miles (112 kilometers) northwest of New York City, and will be put on public display next year.


Lizards are ancient creatures. They were around before the dinosaurs and persisted long after dinosaurs went extinct. We’ve now found they are 35 million years older than we thought they were.
Cryptovaranoides microlanius was a tiny lizard that skittered around what is now southern England during the late Triassic, around 205 million years ago. It likely snapped up insects in its razor teeth (its name means “hidden lizard, small butcher”). But it wasn’t always considered a lizard. Previously, a group of researchers who studied the first fossil of the creature, or holotype, concluded that it was an archosaur, part of a group that includes the extinct dinosaurs and pterosaurs along with extant crocodilians and birds.
Now, another research team from the University of Bristol has analyzed that fossil and determined that Cryptovaranoides is not an archosaur but a lepidosaur, part of a larger order of reptiles that includes squamates, the reptile group that encompasses modern snakes and lizards. It is now also the oldest known squamate.
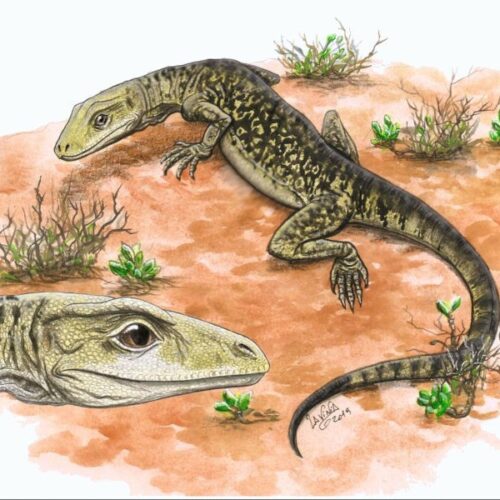
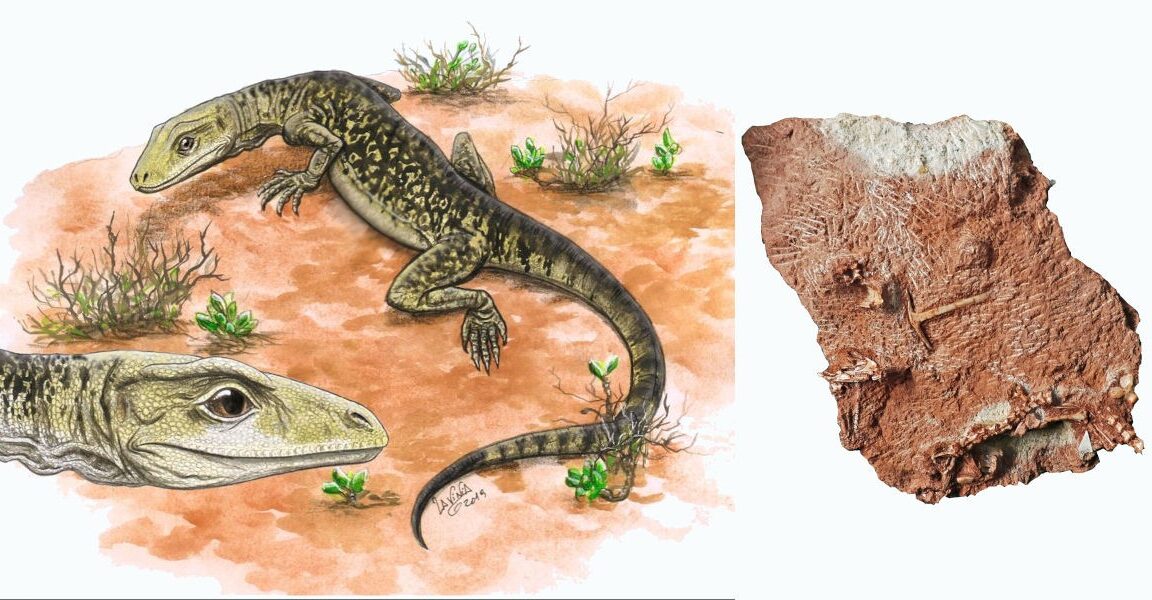
© Lavinia Gandolfi/David Whiteside, Sophie Chambi-Trowell, Mike Benton and the Natural History Museum, London

Paleontologists have long puzzled over how the dinosaurs—originally relatively small and of minor importance to the broader ecosystem—evolved to become the dominant species some 30 million years later. Fossilized feces and vomit from dinosaurs might hold important clues to how and why this evolutionary milestone came about, according to a new paper published in the journal Nature.
Co-author Martin Qvarnström, an evolutionary biologist with Uppsala University in Sweden, and his collaborators studied trace fossils known as bromalites, a designation that includes coprolites as well as vomit or other fossilized matter from an organism's digestive tract. As previously reported, coprolites aren't quite the same as paleofeces, which retain a lot of organic components that can be reconstituted and analyzed for chemical properties. Coprolites are fossils, so most organic components have been replaced by mineral deposits like silicate and calcium carbonates.
For archaeologists keen on learning more about the health and diet of past populations—as well as how certain parasites evolved in the evolutionary history of the microbiome—coprolites and paleofeces can be a veritable goldmine of information. For instance, in 2021 we reported on an analysis of preserved paleo-poop revealing that ancient Iron Age miners in what is now Austria were fond of beer and blue cheese.


© Marcin Ambrozik

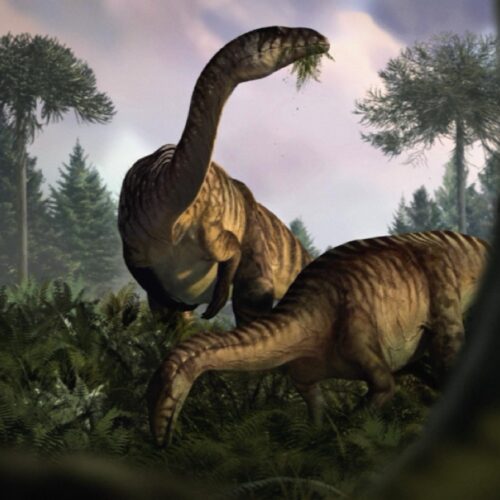
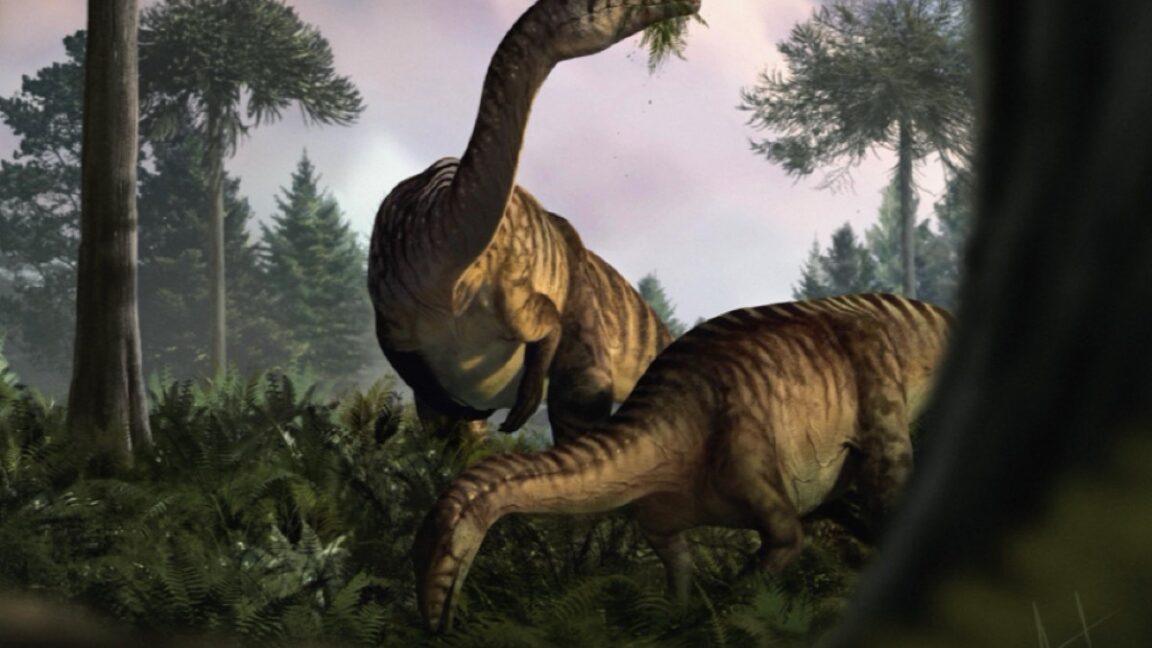
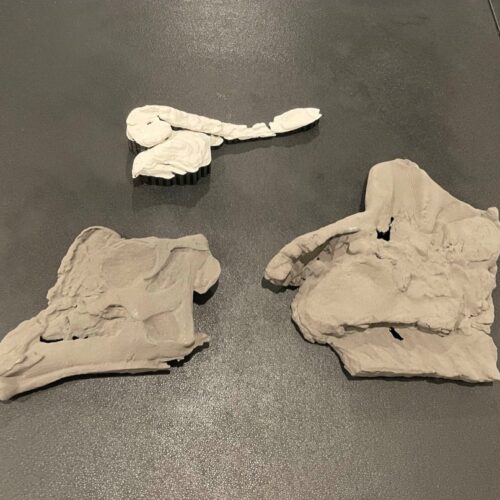
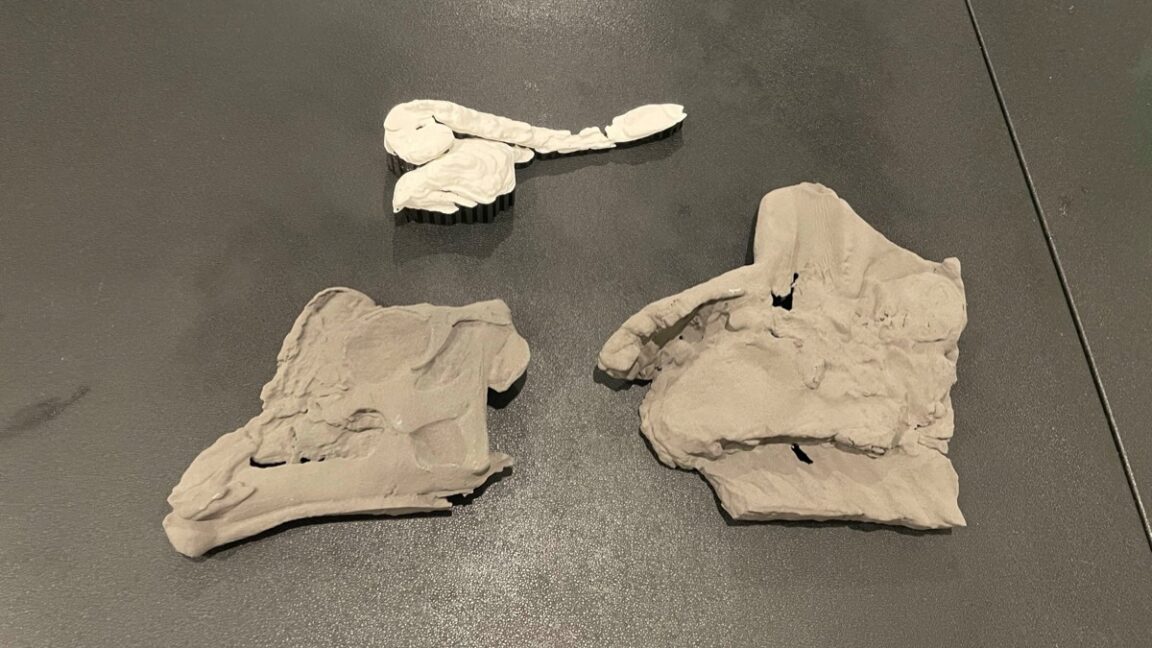
The duck-billed dinosaur Parasaurolophus is distinctive for its prominent crest, which some scientists have suggested served as a kind of resonating chamber to produce low-frequency sounds. Nobody really knows what Parasaurolophus sounded like, however. Hongjun Lin of New York University is trying to change that by constructing his own model of the dinosaur's crest and its acoustical characteristics. Lin has not yet reproduced the call of Parasaurolophus, but he talked about his progress thus far at a virtual meeting of the Acoustical Society of America.
Lin was inspired in part by the dinosaur sounds featured in the Jurassic Park film franchise, which were a combination of sounds from other animals like baby whales and crocodiles. “I’ve been fascinated by giant animals ever since I was a kid. I’d spend hours reading books, watching movies, and imagining what it would be like if dinosaurs were still around today,” he said during a press briefing. “It wasn’t until college that I realized the sounds we hear in movies and shows—while mesmerizing—are completely fabricated using sounds from modern animals. That’s when I decided to dive deeper and explore what dinosaurs might have actually sounded like.”
A skull and partial skeleton of Parasaurolophus were first discovered in 1920 along the Red Deer River in Alberta, Canada, and another partial skull was discovered the following year in New Mexico. There are now three known species of Parasaurolophus; the name means "near crested lizard." While no complete skeleton has yet been found, paleontologists have concluded that the adult dinosaur likely stood about 16 feet tall and weighed between 6,000 to 8,000 pounds. Parasaurolophus was an herbivore that could walk on all four legs while foraging for food but may have run on two legs.


© Hongjun Lin