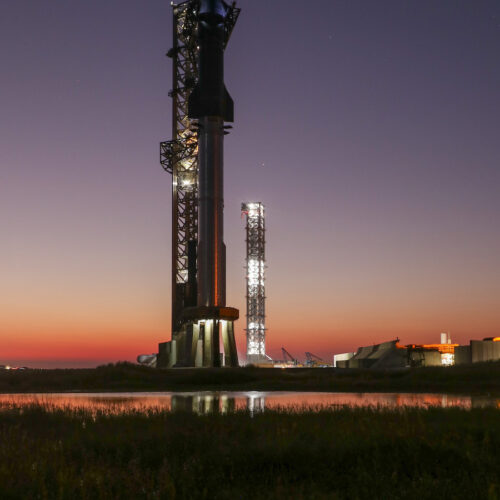
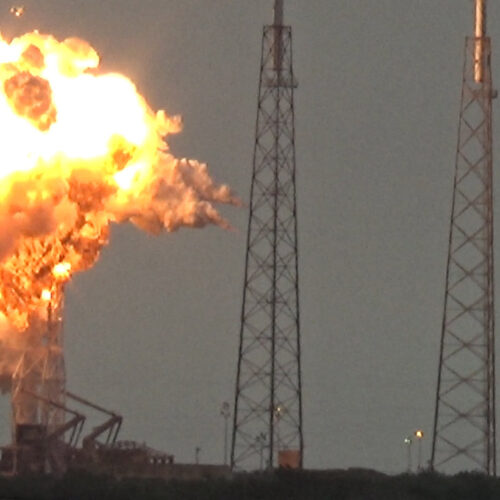
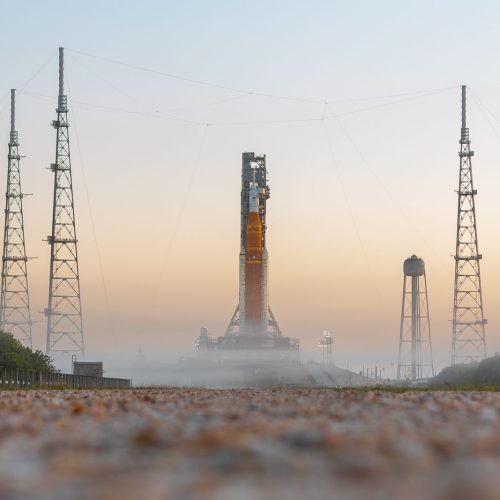
Rocket Report: How is your payload fairing? Poland launches test rocket.
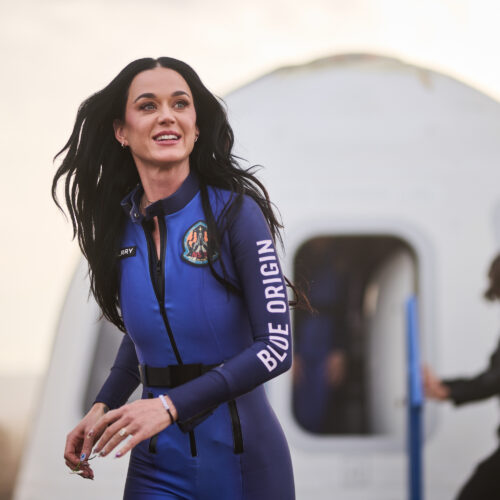
Welcome to Edition 7.44 of the Rocket Report! We had some interesting news on Thursday afternoon from Down Under. As Gilmour Space was preparing for the second launch attempt of its Eris vehicle, as part of the pre-launch preparations, something triggered the payload fairing to deploy. We would love to see some video of that. Please.
As always, we welcome reader submissions, and if you don't want to miss an issue, please subscribe using the box below (the form will not appear on AMP-enabled versions of the site). Each report will include information on small-, medium-, and heavy-lift rockets, as well as a quick look ahead at the next three launches on the calendar.

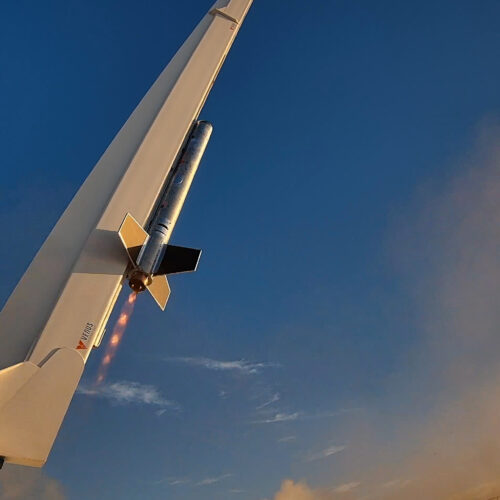
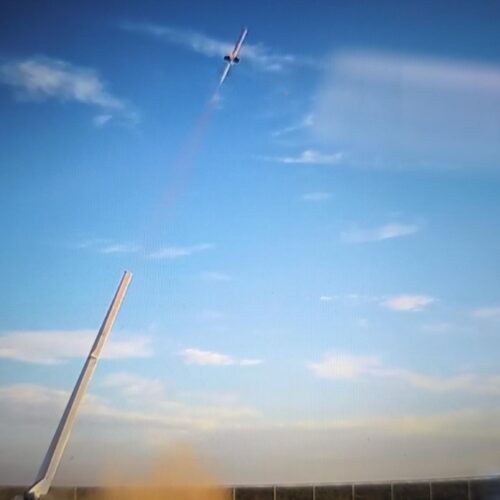
Rotating detonation rocket engine takes flight. On Wednesday, US-based propulsion company Venus Aerospace completed a short flight test of its rotating detonation rocket engine at Spaceport America in New Mexico, Ars reports. It is believed to be the first US-based flight test of an idea that has been discussed academically for decades. The concept has previously been tested in a handful of other countries, but never with a high-thrust engine.


© Venus Aerospace